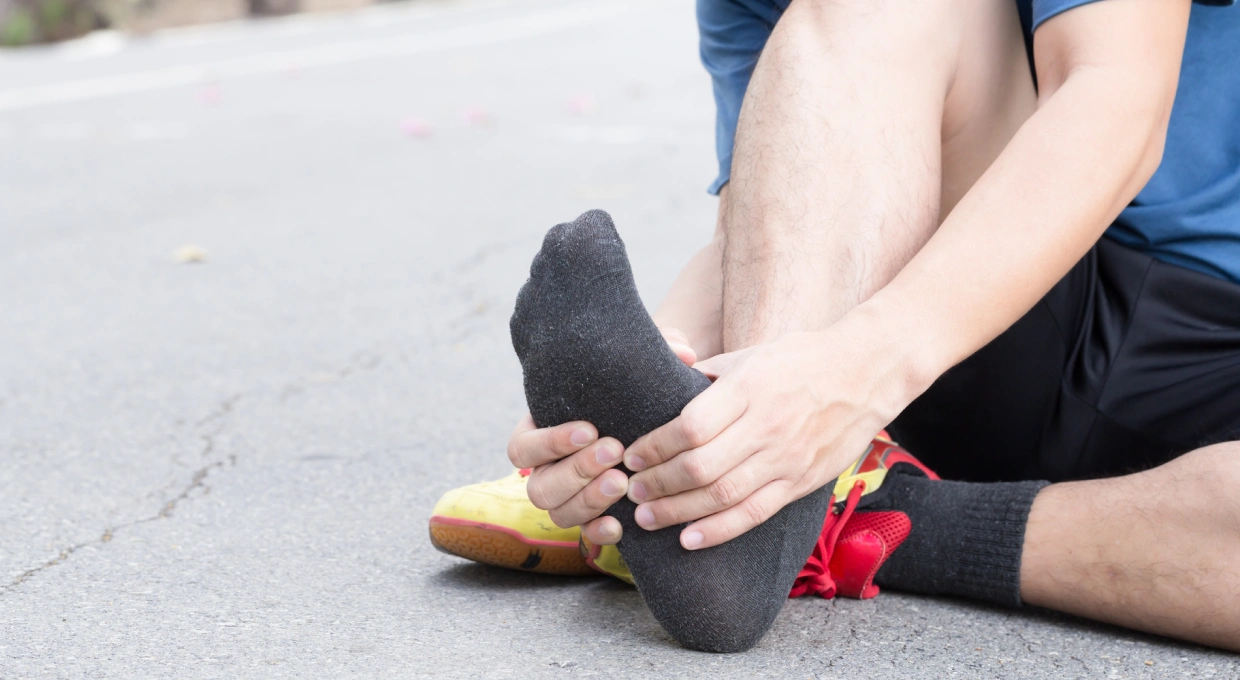
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common injuries among athletes, both amateur and professional. This condition affects the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the sole of the foot, connecting the heel to the toes. Inflammation of this fascia causes a sharp pain in the heel, especially when taking the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest.
What Causes Plantar Fasciitis in Athletes?
In athletes, plantar fasciitis is usually the result of repetitive overuse of the plantar fascia. Some common causes include:
- Intense Training Overload: Sudden increases in training intensity or duration can place excessive pressure on the plantar fascia, causing microtears that lead to inflammation.
- Inadequate Footwear: Shoes that do not provide good arch support or adequate shock absorption may increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
- Flat Feet or High Arches: People with high arches or flat feet are more prone to plantar fasciitis due to improper weight distribution in the foot.
- Hard Surfaces: Running or training on hard surfaces without adequate cushioning can contribute to the development of this condition.
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis
The main symptom of plantar fasciitis is a sharp pain in the bottom of the heel, often described as a prickling or burning sensation. This pain is most intense when getting up in the morning or after sitting for a while. Other symptoms may include:
- Pain that decreases with activity: Although the pain usually decreases after the first few steps, it may return after intense or prolonged activity.
- Heel stiffness: The heel may feel stiff, especially at the beginning of the day or after being inactive.
- Tenderness in the sole of the foot: Touching the sole of the foot may be painful, especially in the area near the heel.
Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis in Athletes
Treatment of plantar fasciitis in athletes focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving pain and preventing further injury. Some common treatment methods include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: It is essential to reduce the load on the affected foot. This may involve decreasing the intensity of training or switching to low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling.
- Use of Ice: Applying ice to the heel for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
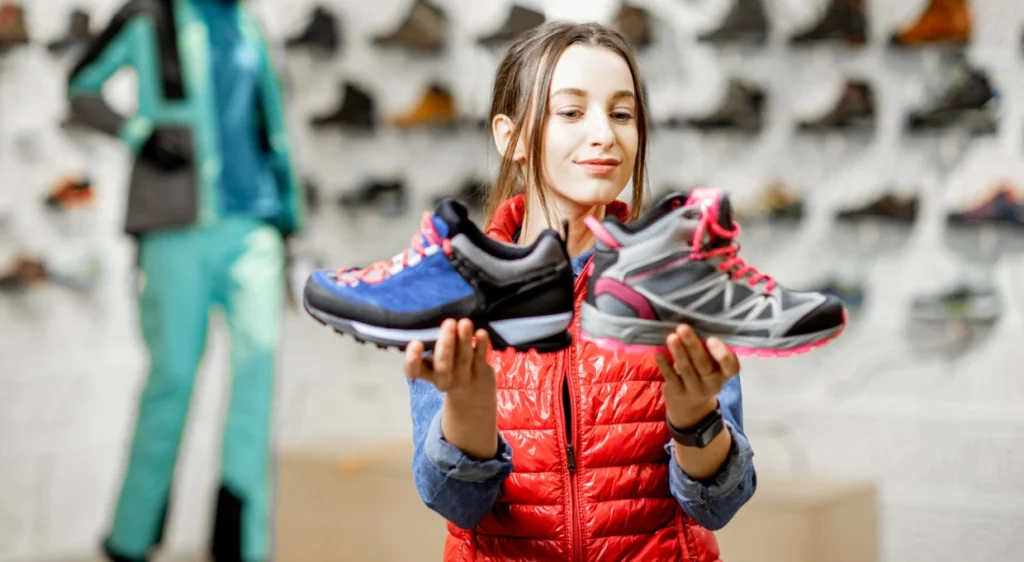
- Footwear and Orthotics: Wearing proper footwear with good arch support and cushioning is essential. Custom orthotics can redistribute pressure on the foot and reduce stress on the plantar fascia.
- Stretches and Exercises: Stretching exercises for the plantar fascia and calf muscles are crucial for improving flexibility and relieving tension. A physical therapist can recommend a specific routine.
- Physical Therapies: Therapies such as electrotherapy, ultrasound therapy or shock wave therapy may be helpful in speeding recovery.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: NSAIDs may be helpful in controlling pain and reducing inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be necessary to reduce inflammation, although their use should be monitored by a specialist due to possible side effects.
Prevention of Plantar Fasciitis in Athletes
Prevention is key to avoiding recurrence of plantar fasciitis. Some tips include:
- Gradual Training Progression: Increasing the intensity and duration of training gradually allows the plantar fascia to adapt to new demands without overloading.
- Proper Footwear: Investing in a good pair of shoes designed for your sport, with proper support and cushioning, can prevent injuries.
- Regular Stretches: Incorporating stretches for the plantar fascia and calf muscles into your daily routine can improve flexibility and reduce stress on the foot.
- Avoid Hard Surfaces: Whenever possible, train on soft surfaces or wear shoes with good cushioning when running on hard surfaces.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy body weight reduces pressure on the feet and decreases the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis is a common injury that affects both amateur and professional athletes. Although it can be painful and limiting, with proper treatment and the right preventative measures, it is possible to fully recover and return to physical activity. If you are experiencing symptoms of plantar fasciitis, it is essential to consult a podiatric specialist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. At Clinica San Roman, we are committed to helping you keep your feet healthy and optimize your athletic performance.