Specialist in Percutaneous Foot Surgery
Founder and Medical Director
Based on verified patient feedback





Recovery after Bunion Surgery: Everything You Need to Know
Recovery after bunion surgery is one of the aspects that most worries patients who are…
What Shoes to Wear After Bunion Surgery: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide
One of the most frequently asked questions after bunion surgery is: what shoes can I…
Quick Guide to Percutaneous Foot Surgery: Everything You Need to Know
What is Percutaneous Surgery? Percutaneous foot surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS) or…
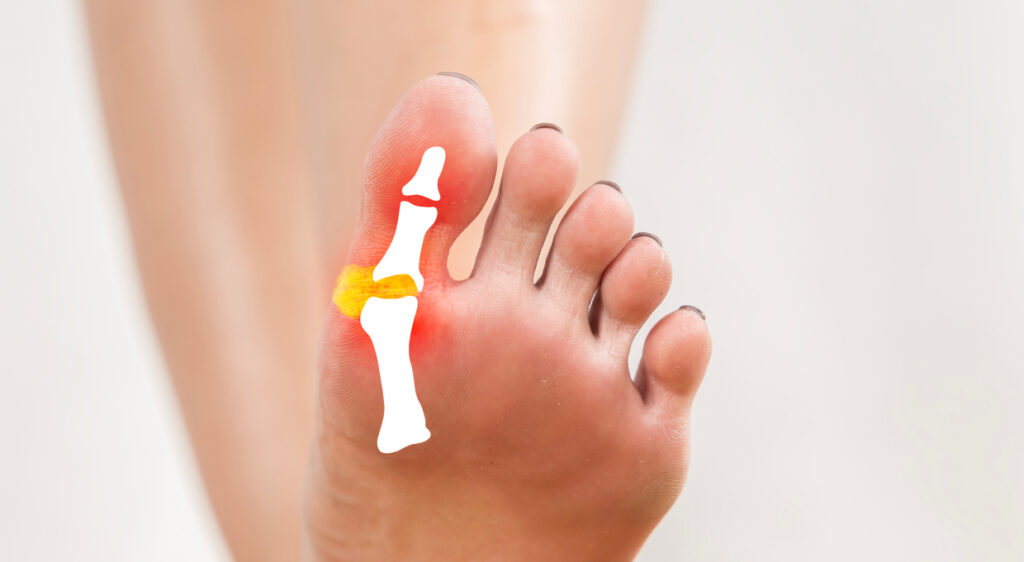
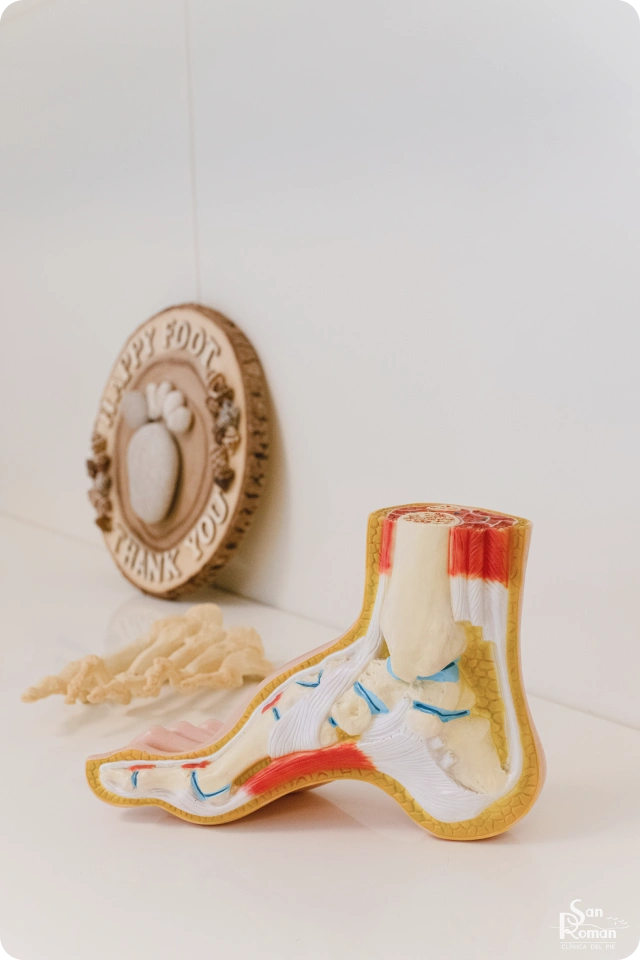
Guide to Hallux Valgus and Percutaneous Surgery
What is bunion (hallux valgus)? The bunion (hallux valgus) is one of the most common…
Achilles tendon rupture: regain your stride without pain or relapse
Achilles tendon rupture is one of the most disabling injuries for any active person. It…
Is it good to walk barefoot on the beach?
Walking barefoot by the sea, with the salty breeze on your face and the sand…
Can wearing flip-flops cause foot injuries?
With the arrival of summer, many people choose flip-flops as their footwear of choice because…
Hardness and Callus Removal
Calluses and corns on the feet are common problems that affect the quality of life…