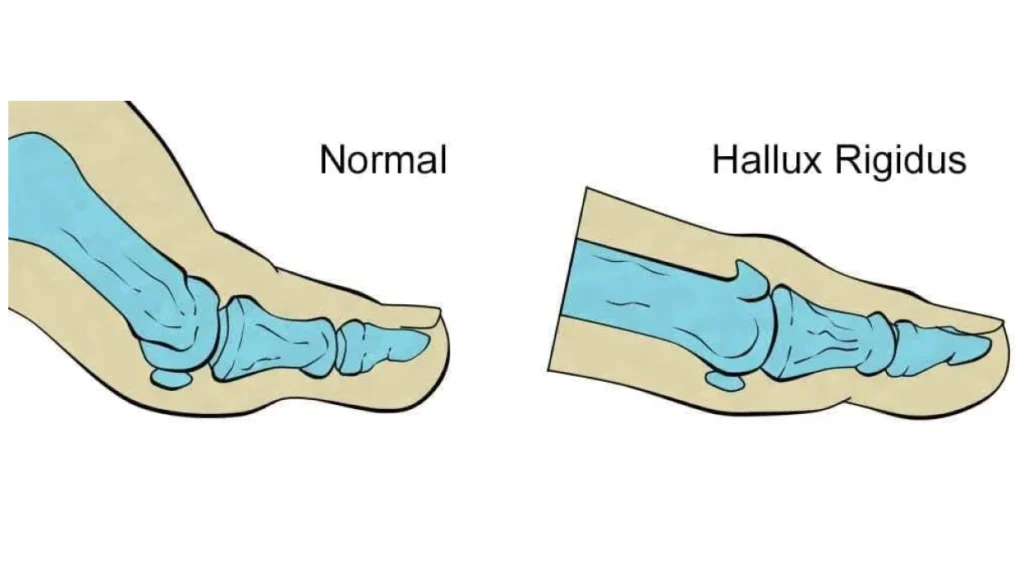
Hallux rigidus is a degenerative condition that affects the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, preventing its normal movement. This condition is a form of osteoarthritis and usually presents symptoms such as pain, stiffness and limitation of motion. Below, we explore in detail what hallux rigidus is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options.
What is Hallux Rigidus?
The term “hallux” refers to the big toe, and “rigidus” indicates stiffness. Therefore, hallux rigidus is characterized by stiffness and pain in the big toe joint, especially during movement. It is a form of arthritis that results in degeneration of the articular cartilage, causing friction between the bones and ultimately loss of mobility.
Causes of hallux rigidus
The causes of hallux rigidus can vary, but generally include:
- Genetics: A genetic predisposition may increase the risk of developing hallux rigidus.
- Trauma: Injuries to the big toe, such as fractures or repetitive sprains, can lead to the development of this condition.
- Structural deformities: High arches, flat feet or abnormal alignment of the big toe can contribute to joint wear and tear.
- Repetitive activities: Sports or jobs involving repetitive movements of the big toe can accelerate the wear and tear of the joint.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hallux rigidus may include:
- Pain and stiffness: Especially when walking, running or standing for long periods.
- Swelling and tenderness: In the affected joint.
- Limited mobility: Difficulty in moving the big toe up and down.
- Development of bone spurs: Bony growths that may appear on top of the big toe joint.
- Changes in gait: Due to pain, people may change the way they walk, which can lead to problems in other areas of the foot, ankles, knees or hips.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of hallux rigidus is made through:
- Physical examination: A podiatrist will evaluate the range of motion of the big toe and look for signs of swelling, tenderness and bony growths.
- X-rays: To visualize the degree of joint degeneration and the presence of bone spurs.
Treatment Options
Treatment of hallux rigidus can be conservative or surgical, depending on the severity of symptoms and progression of the disease.
Conservative Treatments
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Appropriate footwear: Use of shoes with rigid soles and ample room for the toes.
- Orthotics: Customized insoles that redistribute pressure and relieve stress on the joint.
- Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Surgical Treatments
If conservative treatments are not effective, surgical options may be considered, such as:
- Cheilotomy: Removal of bone spurs to improve joint movement.
- Arthrodesis: Fusion of the big toe joint to eliminate pain.
- Arthroplasty: Replacement of the damaged joint with a prosthesis.
Prevention
Although it is not always possible to prevent hallux rigidus, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Use of appropriate footwear: Shoes that provide support and sufficient space for the toes.
- Injury prevention: Foot protection during sports activities.
- Weight control: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the joints of the foot.
Conclusion
Hallux rigidus is a painful and debilitating condition that can significantly affect quality of life. However, with early diagnosis and proper treatment, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve foot function. If you experience pain or stiffness in your big toe, it is essential to consult a podiatric specialist for proper evaluation and treatment.