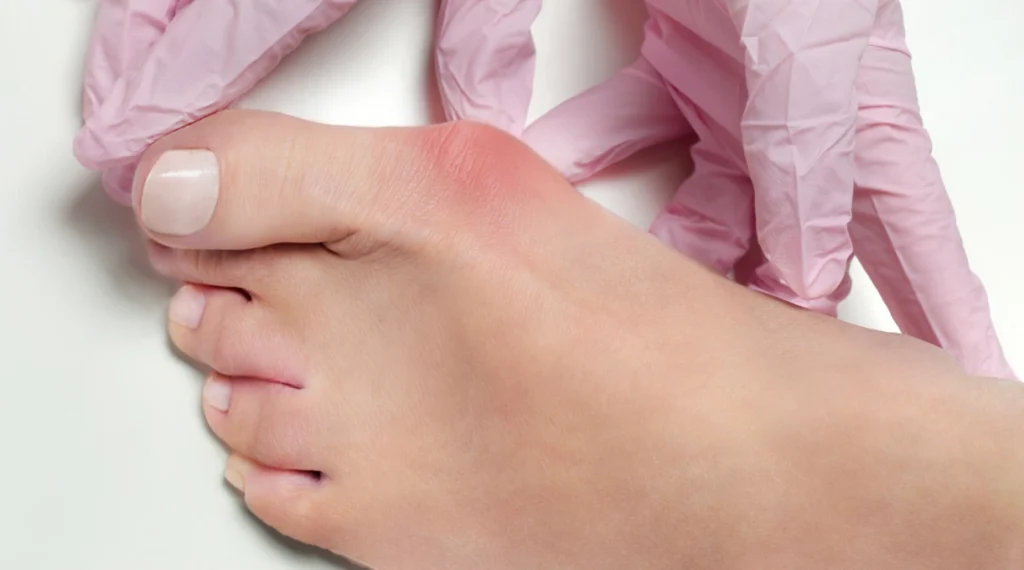
Foot surgery is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on correcting various foot deformities and conditions using advanced techniques. Below, we will explore in detail the types of surgeries, their benefits, complications and postoperative care, to provide a comprehensive and useful guide for those interested in this procedure.
Types of Foot Surgery
Hallux Valgus Surgery (Bunions) Hallux valgus, commonly known as bunion, is one of the most common deformities. Bunion surgery can be performed using minimally invasive techniques (MIS) that allow for precise corrections with less damage to surrounding tissues. MIS for bunions is performed through small incisions, which significantly reduces recovery time and the risk of complications. Claw and Hammer Toe Surgery Finger deformities, such as claw and hammertoes, can also be corrected by minimally invasive surgery. These techniques allow realignment of the fingers with less trauma and faster recovery time compared to traditional surgeries. Plantar Fasciitis and Calcaneal Spurs Plantar fasciitis and heel spurs are common causes of heel pain. Surgery for these conditions includes release of the plantar fascia or removal of the bone spur, using techniques that minimize invasiveness and speed recovery.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS)
Reduced Tissue Damage MIS avoids direct exposure of internal tissues and minimizes vascular damage, which is especially beneficial for patients with circulatory problems or diabetes. Rapid Recovery Patients can walk shortly after surgery due to less invasiveness and the absence of tourniquets, which also reduces the risk of deep vein thrombosis. Reduced Risk of Complications Reduced tissue damage and the precision of MIS techniques significantly reduce the risk of infections and other postoperative complications.

Potential Complications
Although complications are rare, they may include: Osteotomy Mobilization. In less than 5% of cases, there may be displacement of the osteotomy, which may require additional correction. Vasculonervous Injuries Small blood vessel ruptures or nerve injuries that are usually temporary and reversible. Transfer Metatarsalgia Injuries to areas adjacent to the surgical procedure, such as small fractures or pain in the adjacent metatarsals.
Postoperative Care
Immediately After Surgery Postoperative footwear with stiff soles and keeping the foot elevated is recommended to reduce swelling. Applying ice locally may help manage initial pain and swelling. First Week The stitches are removed after 7 days and the bandages are changed. It is crucial to keep the operated area clean and dry to prevent infection. Six Weeks After Surgery The bandages are removed and a radiological evaluation is performed to ensure proper bone healing. Normal footwear can be started according to the patient’s tolerance. Recovery Exercises Perform gentle flexion and extension movements of the first finger to restore joint mobility. These exercises should be performed several times a day, following the doctor’s instructions.
Conclusion
Foot surgery, especially through minimally invasive techniques, offers an effective solution for various foot deformities and conditions, with significant benefits in terms of recovery and reduced complications. At