Foot surgery experts: bunions and claw toes
At Clínica San Román, located in the heart of Alicante, we specialize in the treatment of foot disorders using advanced and minimally invasive techniques.
We are leaders in percutaneous foot surgery, addressing problems such as bunions and claw toes with effective results and rapid recovery.
Our Services:
– Percutaneous foot surgery: Minimally invasive techniques that guarantee less pain and shorter recovery times.
– Comprehensive podiatry: Evaluation and treatment of all types of foot pathologies.
– Preventive medicine: Prevention of deformities and maintenance of podiatric health.
– Personalized treatment: Integral approach adapted to each patient.
More than 45 years of family experience.
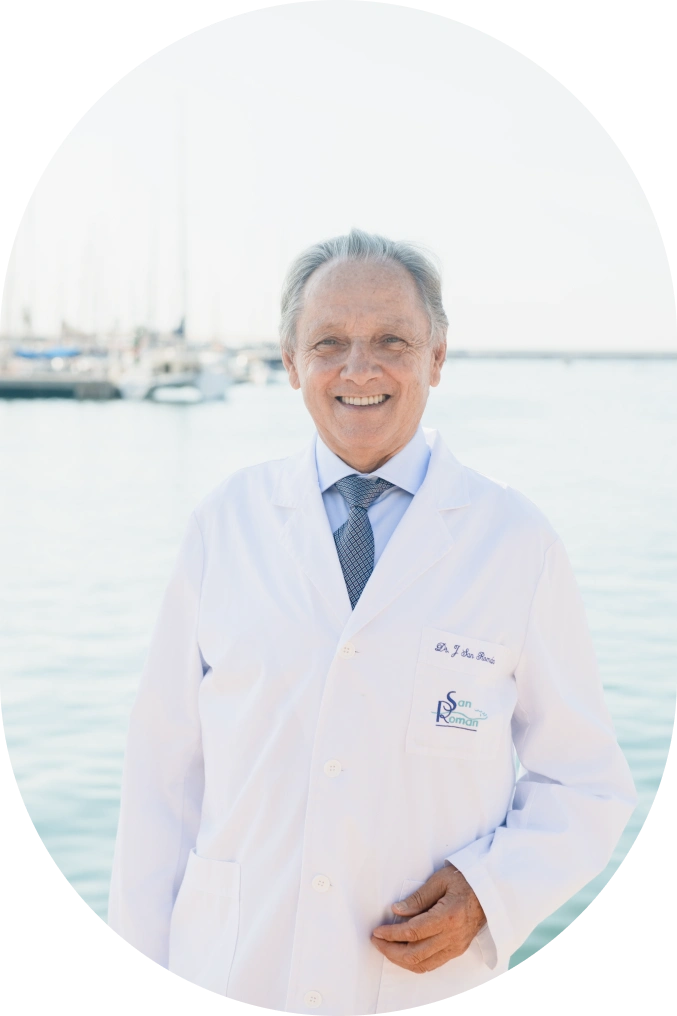
Since 1979, Clínica San Román has been a reference in Europe thanks to Dr. José Manuel San Román Pérez, pioneer in percutaneous foot surgery. His legacy continues with a familiar and close approach, always up to date with the latest medical innovations.
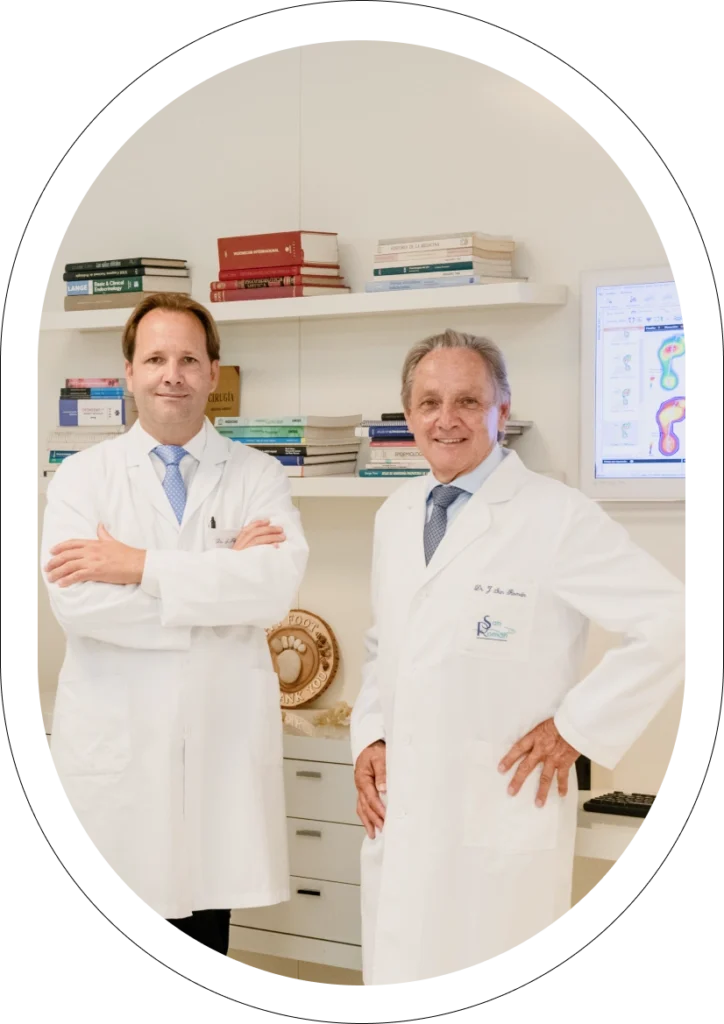


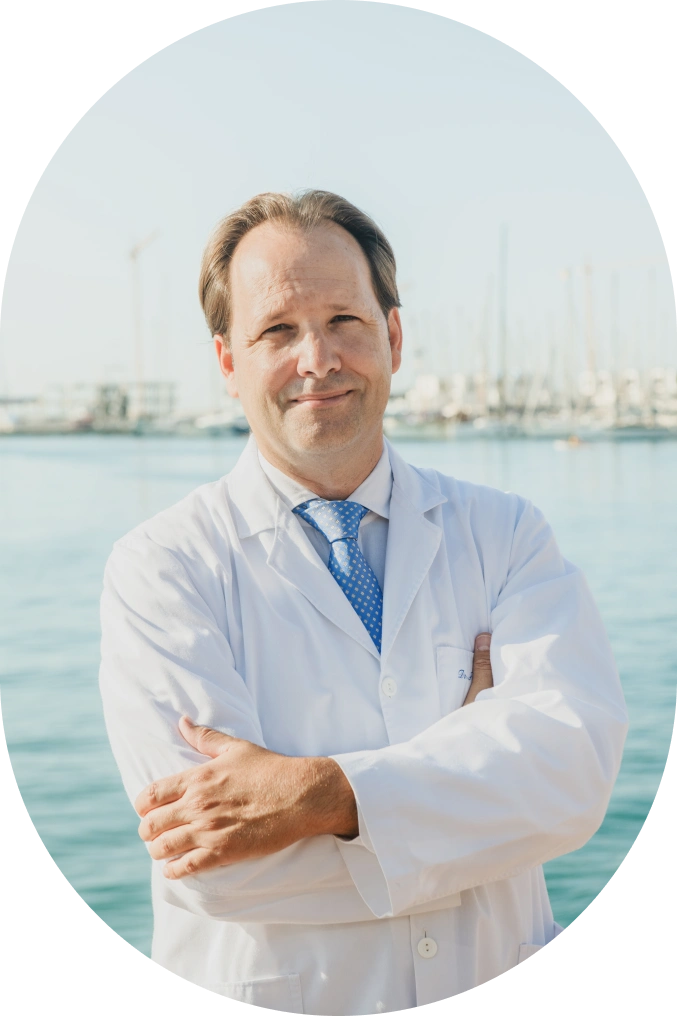
San Roman Clinic Medical Team
At Clínica San Román we have a first class medical and podiatric team, led by Dr. San Román, experts in minimally invasive or percutaneous surgery for the treatment of foot deformities, especially bunions and claw toes.
Doctors San Roman stand out for being the first specialists in Europe to obtain the subspecialty in minimally invasive foot surgery granted by the American Board of Multiple Specialties in Podiatry (Certificate Number: MIS23BE03). In addition, since 1986, they hold the prestigious title of “Fellow” of the American Academy of Ambulatory Foot and Ankle Surgery in the USA.
They are also active members of various foot surgery associations in Spain and Europe, collaborating in research projects and advanced studies with the Foot Surgery and Study Group (GRECMIP) and the American Association for Minimally Invasive Foot and Ankle Surgery (AMIFAS) in the USA.
Recognized for Medical Excellence
At Clínica San Román, we have been constantly nominated for the TopDoctors Awards, a recognition of the specialists best rated by patients and by a medical committee.
Current score in TopDoctors:
TOPDOCTORS:
Based on verified patient feedback
Discover Clínica San Román
We want you to get a close look at how we work and what you can expect when you visit us. In this video, we show you our facilities, our medical team, and how we approach each case in a personalized way.
We specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of all types of foot problems, from common ailments to surgical procedures using minimally invasive techniques. We are committed to providing close, unhurried care focused entirely on you.
If you experience discomfort while walking or are looking for a definitive solution for your feet, this is the place for you. Hit play and get to know us.

Quality and Reliability at San Roman Clinic
At Clínica San Román we guarantee the highest quality and safety in all our medical, podiatric and minor foot surgery treatments. Our clinic is duly registered and regulated by Health, with the Certificate of Registration number 5357 in the Autonomous Registry of Centers, Services and Health Establishments of the Valencian Community, which guarantees our commitment to medical excellence.
We have modern facilities in the center of Alicante, which rigorously comply with asepsis and hygiene regulations. All our areas are supervised weekly by Actualia, ensuring a safe and risk-free environment for our patients.
In addition, we strictly follow the Royal Decree 487/2022 for the prevention and control of Legionella bacteria, which allows us to offer a clinical environment of total confidence and safety.
Our state-of-the-art equipment for the diagnosis and treatment of foot pathologies complements our comprehensive approach, giving each patient the peace of mind of receiving care with the highest quality standards.
Specialized Treatments at Clínica San Román
At Clínica San Román, we offer advanced and personalized solutions for the treatment of various foot conditions. Our medical and podiatric team, highly specialized in medicine, surgery and podiatry, addresses with excellence both deformities and joint pain as well as complex biomechanical problems.
We use the most innovative and effective techniques, always backed by the latest scientific evidence, to ensure a fast and safe recovery. Our main objective is to improve your quality of life, relieving pain and restoring the functionality of your feet so that you can resume your daily activities with total normality and without discomfort.
Below this section, you will find an interactive search engine with the most frequent foot deformities and pathologies that we treat in our clinic. This tool will allow you to quickly identify your problem and directly access detailed information about the specific treatments we offer.
We invite you to discover the ideal treatment for you and take the first step towards a pain-free life, with the confidence and security that only Clínica San Román, with more than 45 years of experience and exclusive dedication to foot care, can offer you.
Recognition and Medical Collaborations
At Clínica San Román, we are proud to have the support and recognition of the main national and international medical associations in podiatry and foot surgery. Our trajectory and commitment to excellence have led us to be members of prestigious institutions that endorse our experience and professionalism.
More than 45 years of experience in foot care
At Clínica San Román, we have more than 45 years of experience in foot surgery and orthopedics, as well as in the comprehensive treatment of all types of foot disorders. Our goal is to offer each patient a perfect balance between optimal results and rapid recovery, ensuring maximum comfort and well-being.
We have a highly qualified nursing team committed to providing personalized and professional care. In addition, our administrative staff will assist you with maximum efficiency in Spanish, English, German and French, facilitating fluid communication and ensuring a satisfactory experience for all our international patients.
We invite you to learn more about our treatments and services through the videos available on our official YouTube channel, where you can discover firsthand the excellence and dedication that characterize Clínica San Román.

The best care in foot surgery and podiatry
Clínica San Román combines experience with the latest technology to offer you the highest quality treatments in podiatry and foot surgery.

What our customers say
The satisfaction of our patients is our best guarantee. Discover their opinions and learn how our treatments have improved their quality of life.
No dudé en acudir a consulta en Julio y, tras conocer a Israel y explicarme el procedimiento, me decidí a operarme en enero.
La intervención se realizó con anestesia local, los dos pies al mismo tiempo y el posoperatorio fue de lo más llevadero, apenas tuve que tomar analgésicos y no se puede hablar de dolor sino de molestias totalmente soportables. Desde el primer día se pueden apoyar los pies en el suelo e ir paulatinamente caminando.
A los 20 días me pude trasladar en tren a mi residencia habitual en Andalucía.
El personal de la clínica es encantador e Israel un gran profesional que inspira tranquilidad y confianza.
Indicar también que esta técnica mínimamente invasiva hay traumatólogos que me aseguraban que no era posible en mis pies.
Es importante acudir a especialistas con un bagaje como el de Clínica San Román.
Thanks
Pero un día conocí está clínica por internet y viendo las buenas opiniones que tenía me decidí a llamar y pedir mi cita para la operación, me dieron muchas confianza,me operaron de los dos pies el mismo día, fue muy rápido y
Salí caminando sin problemas,la recuperación fue muy rápida,y el resultado increíble, hicieron muy buen trabajo ,estoy muy contenta.
Y por supuesto destacar el buen trato y amabilidad de los doctores y todo el personal de la clínica San Roman.
Este ha sido el resultado,los dos pies de juanetes y seis dedos en garra.
niks als lof over deze kliniek !!!!
de arts is heel begaan met de patiënten , een arts die zijn vakgebied kent en jaren ervaring
Het hele team is zorgzaam en geen vraag is te veel
Na de operatie zijn ze dag en nacht bereikbaar
Voor vragen
En ook bij thuiskomst is er geregeld contact
Om te weten of alles goed gaat
Vragen worden meteen beantwoord
Speciale dank aan Carla die altijd vriendelijk mijn vragen beantwoord en mij altijd meteen terug bericht!
San Roman ,dankjullie wel!
Groet van een tevreden klant
Mocht ik in Alicante zijn kom ik zeker met trots mijn mooie voet laten zien
Dank
Incredible and painless results
“I had been suffering from bunions for years and I was afraid to have surgery. At Clínica San Román they explained everything in detail and I opted for minimally invasive surgery. I walked out the same day! The recovery was fast and painless. 100% recommended.”
– María G.
Professionalism and exceptional service
“From the first consultation I noticed that I was in the hands of real specialists. They performed a study of my footprint and now I use customized insoles that have eliminated my foot pain. Impeccable and personalized attention.”
– Carlos R.
The best decision for my health
“I was diagnosed with Morton’s Neuroma and the pain was unbearable. After treatment at Clínica San Román, I walked again without discomfort. The medical team is excellent and very close. Thank you for giving me back my mobility!”
– Ana M.
Benefits of our minimally invasive surgery

Our patients are the fundamental pillar of our activity. As podiatrists and doctors we strive every day to provide them with a professional service according to their needs in a comprehensive and personalized way.
Doctors San Roman will explain in detail the future results of the surgical treatment according to your medical condition, since these may vary from one patient to another as it happens in the different medical specialties that work directly with the human body.
Advantages of our surgical treatments

Follow us on Instagram
Find out more about our treatments, success stories and foot care tips. Join our community and stay up to date with the latest news.
Articles and News
The latest news, perspectives and insights from Clinica San Roman
Find out what we’re doing to keep you safe, read expert articles and interviews with our leading specialist consultants, learn more about common conditions and get answers to your questions.
Hardness and Callus Removal
Calluses and corns on the feet are common problems that affect the quality of life…
Is it advisable to wear second-hand shoes?
The rise of the circular economy and sustainable practices has boosted interest in reusing products,…
Eczema and Psoriasis on Feet
Eczema and psoriasis on the feet are two common dermatological conditions that, although they share…
Are podiatrists doctors in Spain? Everything you need to know about their training and competencies.
It is common for many people to wonder: are podiatrists doctors in Spain? The doubt…
What muscles are in the foot? A complete guide to understand their function and care
The foot is a biomechanical marvel. It supports the entire weight of the body, adapts…
Brown toenail: causes, diagnosis and podiatric treatment
Brown nails is a clinical condition that is of concern to many patients, especially when…
How to maintain good foot hygiene at home
Foot hygiene is a fundamental pillar in maintaining foot health, preventing infections, avoiding discomfort and…
10 signs that you need medical attention for your feet
The feet support our body day after day, but we rarely give them the medical…