The Achilles tendon is the strongest tendon in the human body, but also one of the most prone to injury, especially in active people. Understanding the most common causes of pain in this tendon is crucial to preventing injury and maintaining good podiatric health. In this article, we will explore the main causes of Achilles tendon pain and injury, as well as provide practical tips for prevention and treatment.
What is the Achilles Tendon?
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscles, the gastrocnemius and soleus, to the heel bone, the calcaneus. This tendon is essential for activities such as walking, running and jumping, as it supports the load of the entire body weight during movement. Due to its location and function, it is under great stress, making it susceptible to injury.
Common Causes of Achilles Tendon Injuries
1. Overloading and Overuse
Repetitive use of the Achilles tendon, especially in high-impact activities such as running, can cause micro-tears in the tendon. These tears, over time, can lead to a condition known as tendonitis, which is inflammation of the tendon.
2. Incorrect Exercise Technique
Improper running technique, such as landing hard on the heel or not having good alignment in the stride, can increase stress on the Achilles tendon. In addition, training on hard or inclined surfaces without proper preparation can aggravate the problem.
3. Inadequate Footwear
Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support, especially in the arch of the foot, can contribute to foot malalignment and increase stress on the Achilles tendon. Shoes with worn soles or that do not cushion adequately can also be a risk factor.
4. Lack of Flexibility and Strength in the Calf Muscles
Stiffness in the calf muscles can limit the range of motion of the ankle and increase stress on the Achilles tendon. Also, lack of strength in these muscles can cause excessive load on the tendon during physical activities.
5. Sudden Changes in Exercise Intensity
Suddenly increasing the intensity or duration of exercise without gradual adaptation can lead to overloading of the Achilles tendon, resulting in microtears and tendonitis.
6. Anatomical Factors
Some individuals may have anatomical predispositions, such as flat feet or high arches, which increase the risk of Achilles tendon injuries. These conditions can alter the biomechanics of the foot and lead to uneven load distribution during physical activity.
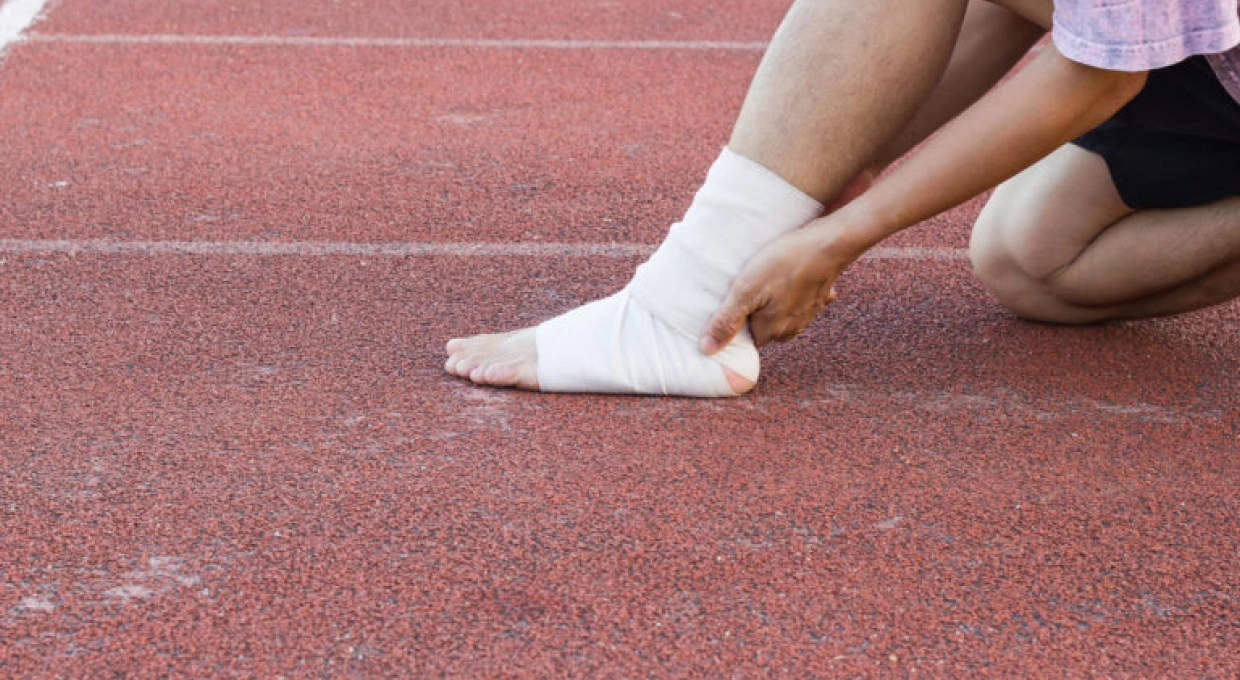

Symptoms of Achilles Tendon Injuries
Achilles tendon injuries can manifest themselves in a variety of ways, depending on the severity of the injury:
- Pain in the back of the heel or along the tendon: This pain may be worse during or after exercise.
- Morning stiffness: It is common to feel stiffness in the Achilles tendon upon awakening, which may improve with activity.
- Swelling or thickening of the tendon: In more severe cases, there may be swelling around the tendon or a palpable nodule in the tendon.
- Inability to bear weight: In severe injuries, such as a tendon rupture, the patient may be unable to bear weight on the affected leg.
Prevention of Achilles Tendon Injuries
Preventing Achilles tendon injuries involves a combination of good exercise habits, proper footwear and muscle strengthening:
1. Warm-up and Stretching
Before any physical activity, a proper warm-up is essential. Incorporating specific stretches for the calf muscles can improve flexibility and reduce stress on the tendon.
Muscle Strengthening
Strengthening exercises for the calf and foot muscles can help to better distribute the load during physical activities, reducing the risk of injury.
3. Gradual Progression in Exercise
Increasing the intensity, duration or frequency of exercise gradually allows the Achilles tendon to adapt to the increased load, minimizing the risk of overload.
4. Use of Appropriate Footwear
Ensuring that footwear is appropriate for the specific activity and provides good support and cushioning can prevent excessive stress on the Achilles tendon.
5. Rehabilitation and Rest
If Achilles tendon pain or discomfort is present, it is important to reduce physical activity and allow the tendon to rest. In cases of tendonitis, physical therapy can be crucial for full recovery.
Treatment of Achilles Tendon Injuries
Treatment for Achilles tendon injuries varies depending on the severity of the injury:
- Conservative treatment: Includes rest, ice application, compression and elevation (the RICE protocol), as well as physiotherapy.
- Physical Therapies: May include specific stretching, massage, and techniques such as electrotherapy or shock wave therapy.
- Surgical intervention: In cases of tendon rupture, surgery may be necessary to repair the tendon.
Conclusion
The Achilles tendon, although robust, is vulnerable to injury if not properly cared for. Taking preventive measures, such as wearing appropriate footwear, muscle strengthening, and gradual progression in exercise intensity, can significantly reduce the risk of injury. In the event of any discomfort or persistent pain, it is essential to consult a podiatric specialist to avoid major complications. At Clínica San Román, we have the experience and technology necessary to treat these types of injuries and help our patients maintain an active and pain-free life.