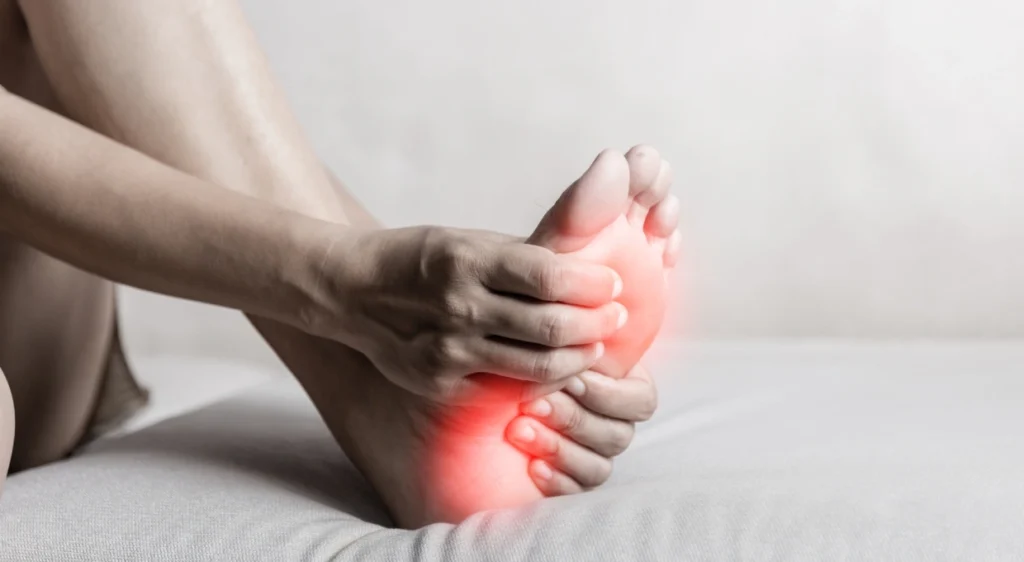
Sesamoiditis is a painful condition that affects the sesamoid bones, two small bones located on the bottom of the foot, just below the big toe. These bones, which are embedded in the tendons, play a crucial role in weight distribution and shock absorption during walking and other physical activities. Inflammation of these bones and surrounding tissues can cause significant pain and limit mobility.
What Causes Sesamoiditis?
Sesamoiditis is usually caused by overuse or repetitive motions that put pressure on the front of the foot. This is common in athletes, dancers and runners, who frequently exert additional force on the metatarsal area. Other risk factors include:
- Inadequate Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or have high heels can increase pressure on the sesamoids.
- Pes Cavus: People with very high arches can put more pressure on the forefoot, which predisposes to inflammation of the sesamoids.
- High Impact Activities: Sports that involve running, jumping or rapid changes of direction can cause irritation of these small bones.
Symptoms of Sesamoiditis
Symptoms of sesamoiditis usually develop gradually, and may include:
- Forefoot Pain: This pain is usually located at the base of the big toe and intensifies during walking, running or any activity that involves putting weight on the forefoot.
- Inflammation: There may be swelling and tenderness in the affected area.
- Difficulty Bending the Big Toe: Movement of the big toe can become painful and limited, affecting gait.
- Pain on Touching the Area: When pressing on the base of the big toe, there may be a sharp pain, which is indicative of inflammation in the sesamoids.
Diagnosis of Sesamoiditis
Diagnosis of sesamoiditis usually involves a combination of physical examination and imaging tests. A podiatrist or foot specialist will examine the foot and press on specific areas to determine the location of the pain. X-rays can help rule out fractures, while an MRI may be helpful in evaluating inflammation in the soft tissues around the sesamoids.
Treatment of Sesamoiditis
Treatment of sesamoiditis is generally conservative and focuses on relieving pressure on the sesamoids and reducing inflammation. Some treatment methods include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that involve pressure on the forefoot is crucial to allow the sesamoids to recover. This may include reducing physical activity or using crutches to avoid weight bearing on the affected area.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
- Use of Orthopedic Insoles: Custom orthopedic insoles can redistribute weight and relieve pressure on the metatarsal area, facilitating recovery.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing shoes with good cushioning and arch support is essential to avoid sesamoid irritation. High heels and narrow shoes should be avoided.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, may be helpful in reducing inflammation and pain in the affected area.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the foot, improve flexibility and reduce the risk of future injury.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In more severe cases, corticosteroid injections may be necessary to reduce inflammation in the sesamoids. However, this treatment is used with caution due to possible side effects.
- Surgery: If conservative treatments are not effective and pain persists, surgery may be necessary. This could involve removal of one or both sesamoid bones, although this is considered a last option due to the risks associated with the intervention.
Sesamoiditis Prevention
The best way to prevent sesamoiditis is to avoid excessive stress on the forefoot. Some preventive measures include:
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Be sure to wear shoes that provide good support and cushioning. Avoid high heels and shoes that do not fit properly.
- Incorporate Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Keeping the foot and calf muscles strong and flexible can reduce pressure on the sesamoids.
- Avoid Overuse: Modifying the intensity and duration of activities that put pressure on the foot, such as running or jumping, can prevent the onset of this condition.
Conclusion
Sesamoiditis is a painful condition that can significantly affect the ability to walk and perform physical activities. Fortunately, with proper diagnosis and a conservative treatment plan, most cases can be managed effectively. If you experience forefoot pain or any other symptoms related to sesamoiditis, it is important to consult a podiatrist or foot specialist to receive proper treatment and avoid long-term complications. At Clinica San Roman, we offer specialized, personalized care to treat sesamoiditis and help you regain your mobility and well-being.