Osteoporosis is a systemic bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone mineral density and deterioration of bone microarchitecture, which increases bone fragility and thus the risk of fractures. Although this condition is commonly associated with the spine, hips and wrists, its effects on the feet and gait are equally significant and often overlooked.
What is osteoporosis and why should you care?
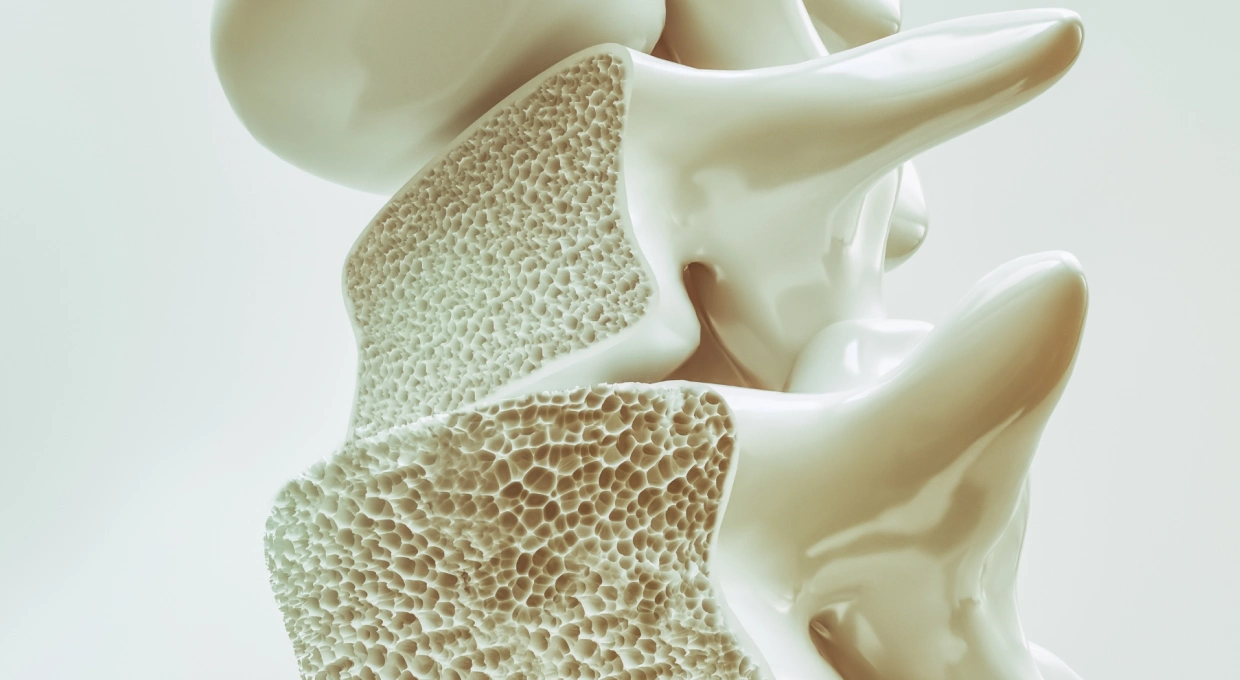
Osteoporosis affects millions of people worldwide, and its prevalence increases with age, especially in postmenopausal women due to declining levels of estrogen, a hormone that protects bones. However, men and younger people can also be affected. It is a “silent disease” because it has no obvious symptoms until a fracture occurs. In the feet, these fractures can be especially problematic because of the constant pressure they bear when walking or standing.
How osteoporosis affects the feet
The feet are complex structures that support body weight, absorb the impact of walking and allow movement. When bone density decreases due to osteoporosis, the bones in the feet, which are already small and delicate, become even more vulnerable. This can lead to stress fractures, which are small cracks in the bone that occur due to repetitive stress or overload. Unlike traumatic fractures, which are the result of a single blow or impact, stress fractures develop gradually over time, making them difficult to detect until pain becomes significant. In particular, metatarsal stress fractures are common in people with osteoporosis. The metatarsal is the group of long bones in the foot that connects the toes to the rest of the foot. These bones are essential for maintaining stability and mobility. A fracture in this area can alter the distribution of weight on the foot, causing pain, swelling and difficulty walking.
Changes in gait and balance
Foot pain and fragility caused by osteoporosis not only affect walking ability, but can also alter gait. A person with osteoporosis may begin to walk more slowly, with shorter strides and a stooped posture to reduce pain and the risk of falling. This altered gait pattern can, in turn, lead to other health problems, such as pain in the knees, hips and lower back due to abnormal weight distribution. In addition, osteoporosis can affect balance. Weak bones, combined with a fear of falling, can cause a person to walk more cautiously, which can actually increase the risk of falls. Falls in people with osteoporosis are particularly dangerous because even a minor impact can result in a serious fracture, such as a hip fracture, which often has devastating consequences.
Prevention and management of osteoporosis of the feet
Preventing and managing osteoporosis is crucial to maintaining foot health and overall mobility. Here are some key strategies:
- Diet Rich in Calcium and Vitamin D: Consuming calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables and soft-boned fish, is essential for maintaining bone health. Vitamin D is equally important, as it helps the body absorb calcium. Safe sun exposure and foods such as fatty fish or supplements can help maintain optimal levels of this vitamin.
- Low Impact Exercise: Although exercise is essential for strengthening bones and improving bone density, it is important to choose activities that do not put undue stress on the feet. Walking, swimming and cycling are ideal exercises for people with osteoporosis. These exercises not only help strengthen bones, but also improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls.
- Proper Footwear: Footwear plays a crucial role in preventing injuries in people with osteoporosis. Shoes should provide good support, cushioning and a stable base to reduce pressure on the bones of the foot. The use of custom orthotics can also help distribute weight more evenly and reduce the risk of stress fractures.
- Regular Podiatric Evaluations: Visiting a podiatrist on a regular basis is essential for people with osteoporosis. A podiatrist can identify changes in the structure of the foot, assess the risk of fractures and recommend treatments or orthotic devices to improve gait and reduce pain.
- Therapies and Drug Treatments: In addition to lifestyle changes, your doctor may recommend medications to treat osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates, for example, are medications that can help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures. There are also newer treatments, such as monoclonal antibodies, which target bone-destroying cells.
Specialized Consultations
If you have osteoporosis and have noticed changes in the way you walk or if you experience pain in your feet, it is essential that you consult a podiatric specialist. A podiatrist who specializes in this field can provide a complete evaluation of your foot health and develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. This plan may include exercises, orthotics, changes in footwear and, in severe cases, surgical options to correct deformities or fractures.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a disease that can severely affect quality of life, especially with regard to mobility and foot health. However, with a preventive approach and proper management, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of fractures and maintain an active and independent life. Don’t hesitate to consult with a specialist if you experience any osteoporosis-related symptoms in your feet, and be sure to follow a routine that includes proper diet, regular exercise and regular medical evaluations to keep your bones strong and healthy.