With the arrival of summer, many people choose flip-flops as their footwear of choice because of their lightness and sense of freedom. However, this apparent comfort can hide risks that affect the health of their feet and, by extension, the entire joint chain. In this article we will examine in detail the anatomy involved, the biomechanical impact of flip-flops, the most common injuries, the factors that increase the likelihood of suffering them and, above all, strategies to minimize damage. Our goal is to provide you with rigorous and practical information so that you can make informed decisions and enjoy the good weather without compromising your well-being.
Foot anatomy and basic biomechanics
The foot is a complex structure made up of 26 bones, 33 joints and more than 100 muscles, ligaments and tendons. Each step requires the precise coordination of all these parts to absorb impact, stabilize the body and propel it forward. An essential component is the plantar arch, which acts as a natural shock absorber and distributes the load between the rearfoot, midfoot and forefoot. When properly designed footwear is used, the sole provides additional support to the arch and reduces pressure on the metatarsals. Flip-flops, on the other hand, lack heel support and provide little or no cushioning, forcing the internal structures to take on constant additional stress.

How the flip-flop alters gait mechanics
The absence of rearfoot support causes the toes to flex continuously to keep the flip-flop in place. This seemingly harmless gesture generates sustained stress on the plantar flexors and alters the way the foot contacts the ground. The heel strikes directly on a thin sole, while the midfoot receives little lateral support, which encourages excessive pronation. The result is an asymmetrical distribution of forces that impacts the ankles, knees and hips. In the medium term, the kinetic chain tries to compensate for the imbalance by adopting postures that overload the lumbar musculature, increasing the risk of low back pain.
Frequent injuries and pathologies
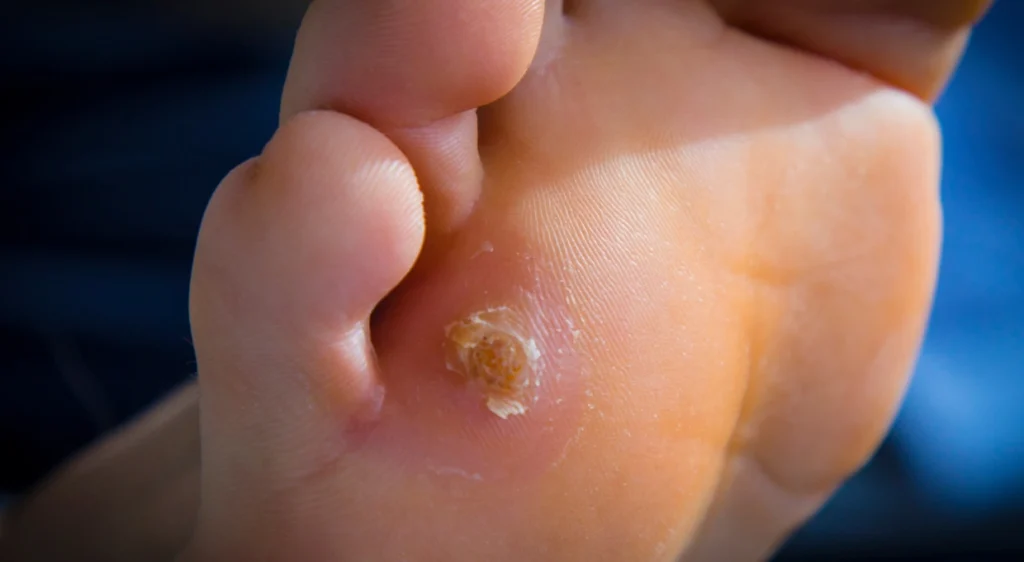
Plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia and Achilles tendinopathy are among the ailments we commonly treat in connection with flip-flops. Plantar fasciitis usually manifests as a shooting pain at the base of the heel when starting the morning walk; metatarsalgia presents as a burning sensation in the forefoot; Achilles tendinopathy is characterized by inflammation and pain in the back of the ankle, especially after physical activity. We also frequently observe blisters, interdigital friction dermatitis and, in prolonged cases, stress fractures of the metatarsals due to repetitive impact on hard surfaces.
Factors that increase the risk of injury
Being overweight increases the force on each foot, amplifying the stress on the soft tissues. People with flat feet or high arches have already compromised biomechanics that flip-flops do nothing to correct. Walking for long periods on rigid surfaces such as concrete or asphalt without proper cushioning multiplies the pressure on the metatarsals. In users with diabetes or vascular problems, decreased plantar sensitivity can hide microtraumas that, if undetected, evolve into difficult-to-treat ulcers.
Warning signs not to be ignored
Pay attention to persistent pain in the heel when getting up, burning sensation in the sole at the end of the day, constant redness between the toes or swelling in the instep. If you notice a limp, progressive increase in pain when walking or the appearance of localized calluses, stop wearing flip-flops immediately and seek professional assessment. Ignoring these signs can turn a mild discomfort into a chronic injury.
Recent scientific studies
Research published in the journal Gait & Posture shows that the continued use of flip-flops increases the duration of foot contact with the ground, altering the kinematics of gait and increasing the axial load on the rearfoot. Another study in the Journal of Foot and Ankle Research observed increased electromyographic activity in the tibialis posterior and toe flexors, corroborating the associated muscle fatigue. These findings support the direct relationship between flip-flops and biomechanical overload, especially in people who exceed two hours of daily use.
Prevention and recommendations for responsible use
Limit flip-flops to short trips, wet environments and moments of rest. If you decide to use them, choose models with a cushioned sole of at least two centimeters, an anatomical insole and a wide strap that holds the forefoot firmly in place. Avoid walking long distances on concrete and try to alternate them with closed shoes with full support. Perform daily calf and plantar fascia stretches, holding each stretch for thirty seconds. Strengthen the intrinsic musculature of the foot by doing exercises such as gripping a towel with your toes or walking barefoot on soft surfaces. Check the size: a flip-flop that is too big forces the toes to flex even more, while one that is too tight increases friction.
Healthy footwear alternatives
Back support sandals with an ergonomic footbed offer a compromise between ventilation and support. For activities that involve walking for hours at a time, opt for sneakers with cushioning and stability control technology. If breathability is a concern, choose technical mesh materials that allow air circulation without sacrificing support. Custom orthotics are an effective solution for those with arch deformities or alterations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I wear flip-flops if I have plantar fasciitis in remission? Only occasionally and for very short intervals, making sure to stretch before and after. Do orthopedic flip-flops eliminate the risk? They reduce some of the overload, but do not replace closed shoes in terms of stability and cushioning. Is it advisable to wear flip-flops in the gym shower? Yes, because they act as a barrier against fungi and bacteria, but you must dry them completely to avoid persistent humidity.
Diagnosis and professional treatment
In case of persistent pain or functional limitation, a complete podiatric examination allows us to identify the exact cause and apply a personalized treatment. At Clínica San Román we have pressure platforms, digital gait analysis and musculoskeletal ultrasound. The comprehensive approach combines physiotherapy, manual therapy, customized insoles and, when appropriate, ultrasound-guided infiltrations. Periodic follow-up ensures lasting improvement and prevents relapses.
Conclusion
Occasional use of flip-flops is perfectly compatible with a healthy lifestyle, as long as it is limited to specific moments and models with the best possible support and cushioning are chosen. However, prolonged use modifies gait mechanics, increases the risk of injury and can trigger chronic pathologies. Recognizing the early signs and adopting preventive habits will be decisive in maintaining the health of your feet.
Do you experience pain, inflammation or discomfort after wearing flip-flops? At Clínica San Román